Hormonal Imbalance Treatment in Korea
Gangnam, Seoul
Restoring Harmony: A Guide to Hormonal Imbalance Treatment in Korea
Hormonal imbalances can manifest in countless ways, from subtle shifts in mood and energy to significant impacts on menstrual cycles, fertility, metabolism, and overall well-being. South Korea, with its advanced medical system and a growing integration of Eastern and Western medicine, offers diverse approaches to diagnosing and treating these complex conditions. If you're an expat in Korea experiencing symptoms of a hormonal imbalance, here’s what you need to know about seeking care.
Common Hormonal Imbalances Treated in Korea
Korean medical professionals regularly treat a wide spectrum of hormonal imbalances. Some of the most common conditions include:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Characterized by irregular periods, excess androgens (leading to acne, hirsutism), and polycystic ovaries. Management often involves lifestyle changes, oral contraceptives, metformin, and fertility treatments. (Refer to our dedicated blog post on PCOS management in Korea for more details).
- Thyroid Disorders:
- Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid, leading to fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and menstrual irregularities.
- Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid, causing weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and heat intolerance.
- Menopause/Perimenopause: The natural decline in estrogen and progesterone, leading to hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, vaginal dryness, and sleep disturbances. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a common treatment.
- Adrenal Disorders: Conditions affecting cortisol production (e.g., Cushing's syndrome, Addison's disease).
- Pituitary Disorders: Imbalances in hormones produced by the pituitary gland, which regulates many other endocrine glands.
- Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI): When ovaries stop functioning normally before age 40, leading to symptoms similar to menopause.
Diagnosis in Korea: A Thorough Approach
Diagnosing a hormonal imbalance in Korea typically involves a comprehensive approach:
- Detailed Medical History & Symptom Assessment: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, lifestyle, and family history.
- Physical Examination: A general physical exam is conducted, focusing on specific signs of hormonal imbalance (e.g., skin condition, hair growth patterns, weight).
- Blood Tests: This is the cornerstone of diagnosis. Specific hormone levels will be measured based on your symptoms:
- Reproductive Hormones: FSH, LH, Estrogen, Progesterone, Testosterone, Prolactin (for menstrual irregularities, fertility issues).
- Thyroid Hormones: TSH, Free T3, Free T4.
- Adrenal Hormones: Cortisol (often timed tests).
- Glucose & Insulin: To assess for insulin resistance, especially in PCOS.
- Imaging Studies:
- Pelvic Ultrasound: Crucial for diagnosing PCOS and assessing ovarian health.
- Thyroid Ultrasound: To examine the thyroid gland for nodules or goiter.
- MRI/CT Scans: May be used to investigate pituitary or adrenal glands if a tumor is suspected.
Korean laboratories are highly efficient, and you can often get blood test results back within a few days.
Treatment Modalities: Western, Eastern, and Integrative
Treatment in Korea is tailored to the specific hormonal imbalance, its underlying cause, and your individual symptoms.
- Conventional Western Medicine:
- Medication: This is the primary approach for many imbalances:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): For menopause (estrogen, progesterone) or low testosterone (for men).
- Oral Contraceptive Pills (OCPs): Often used for PCOS to regulate periods and manage androgen excess.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement: For hypothyroidism.
- Anti-thyroid Medications or Radioactive Iodine: For hyperthyroidism.
- Metformin: For insulin resistance, common in PCOS.
- Anti-androgens: To address excess male hormones.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Korean doctors place a strong emphasis on diet, exercise, and stress management as foundational to hormonal balance, especially for conditions like PCOS and pre-diabetes. You may be referred to a nutritionist.
- Surgery: In cases of tumors (e.g., thyroid nodules, pituitary adenomas, adrenal tumors) affecting hormone production, surgery may be recommended.
- Traditional Korean Medicine (TKM - Hanbang 한방):
- TKM offers a complementary perspective, aiming to restore overall bodily balance (Qi, Yin/Yang, Five Elements). Many individuals in Korea choose to integrate TKM with Western treatments.
- Herbal Medicine: Custom-formulated herbal concoctions are prescribed to address specific imbalances, improve organ function (especially liver, kidney, spleen in TKM), regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce symptoms.
- Acupuncture & Moxibustion: These therapies are used to stimulate specific points to improve energy flow, blood circulation, reduce stress, and influence hormonal pathways.
- Dietary & Lifestyle Counseling: TKM practitioners provide personalized advice on diet and lifestyle specific to your body's "constitution" (e.g., Sasang constitutional medicine).
- Integrative Approaches:
- Some clinics in Korea specialize in combining Western diagnostic methods with TKM therapies, offering a holistic approach to complex hormonal conditions. This can be particularly appealing for those seeking comprehensive care.
Who to See: Specialists in Korea
For hormonal imbalances, you'll primarily consult with:
- Endocrinologists: Specialists in the endocrine system, treating conditions like thyroid disorders, diabetes, pituitary and adrenal disorders. Major university hospitals will have strong Endocrinology departments.
- OB/GYN (Obstetrics and Gynecology) Doctors: For hormonal imbalances specifically related to reproductive health, such as PCOS, menopause, irregular periods, and infertility. Many women's health clinics specialize in these areas.
Cost of Treatment in Korea
Costs can vary widely. While initial consultations and some diagnostic tests (like basic blood work if medically indicated) are partially covered by the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) for those enrolled, many ongoing treatments, particularly for long-term conditions or specific medications not on the general formulary, may require out-of-pocket payment.
- Initial Consultation (with NHIS): ₩5,000 - ₩20,000 KRW. (without NHIS): ₩30,000 - ₩100,000+ KRW.
- Hormone Blood Tests (per test, without NHIS): Can range from ₩10,000 to ₩50,000+ KRW per specific hormone, potentially adding up for a full panel. With NHIS, the co-pay is much lower.
- Medications (per month): Highly variable. OCPs and metformin can be relatively inexpensive even without full coverage, but specialized HRT or infertility medications can be more costly.
- TKM Treatments: Often out-of-pocket. Herbal medicine can range from ₩100,000 to ₩300,000 KRW or more per week/month. Acupuncture sessions typically ₩30,000 to ₩70,000 KRW per session.
Always discuss potential costs and coverage with your doctor and clinic staff upfront.
For Expats: Navigating the System
- Language Barrier: This is the most common challenge.
- International Health Centers: Major university hospitals (Severance, Asan, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul St. Mary's, CHA Gangnam Medical Center) have dedicated international departments with English-speaking staff and doctors. These are often the best starting point for complex or chronic conditions.
- Private Clinics: Many private OB/GYN or internal medicine clinics in expat-dense areas (Gangnam, Itaewon, Hannam-dong) have English-speaking staff. Check online reviews and expat forums for recommendations.
- Translation Apps/Friend: Always have a translation app (like Papago) handy, or consider bringing a Korean-speaking friend for important appointments.
- Continuity of Care: Hormonal imbalances often require ongoing management. Establishing a long-term relationship with a trusted doctor is crucial.
- Bringing Records: If you have prior diagnoses or test results from your home country, bring them (translated into English if possible) to provide your Korean doctor with a comprehensive medical history.
By understanding the available diagnostic and treatment options and proactively seeking out foreigner-friendly medical facilities, you can effectively manage hormonal imbalances and achieve better health outcomes in Korea.
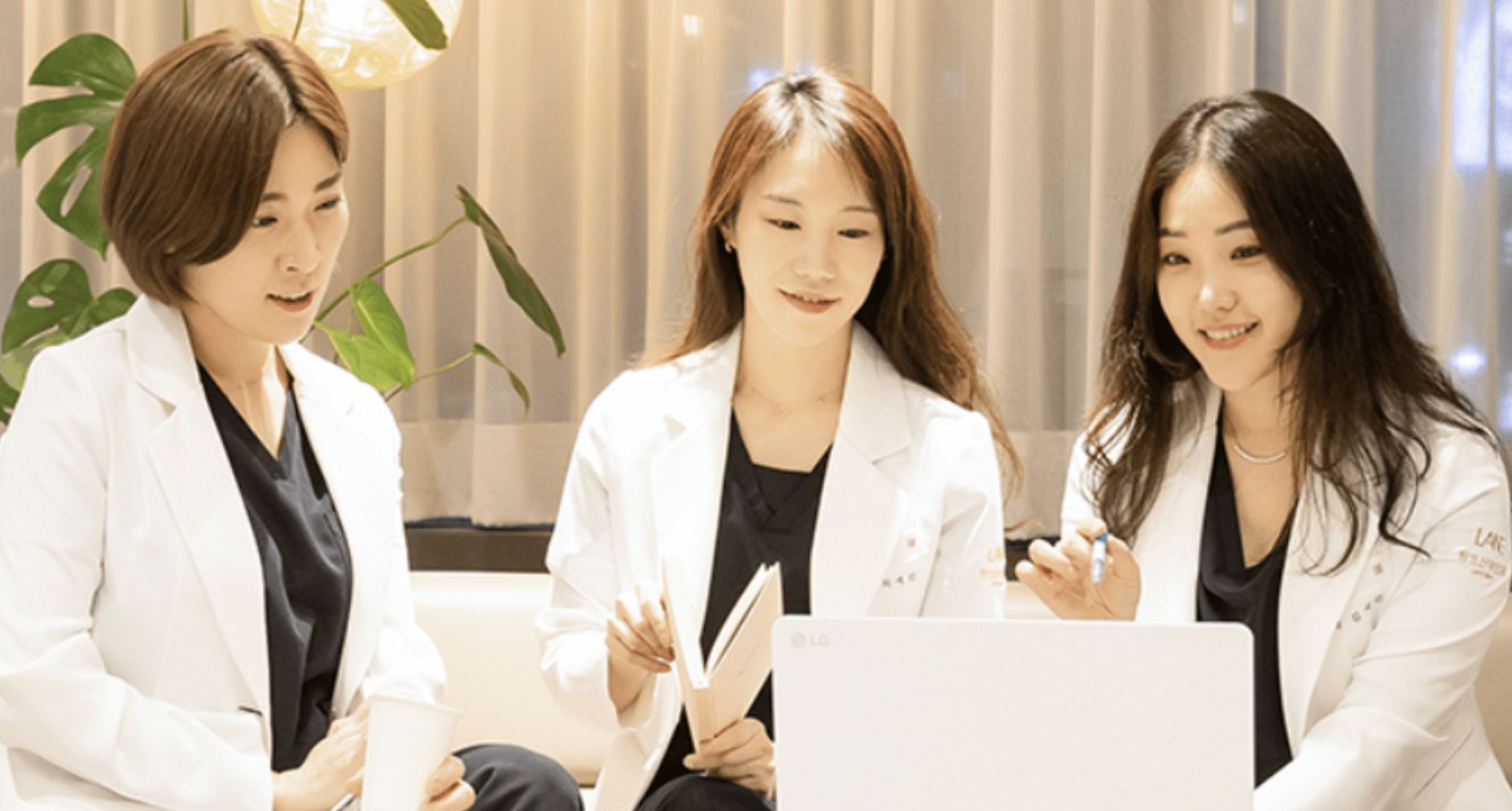

The female director personally provides care, listening to each patient's story.
01 - One-on-One Personalized Treatment
02 - Post-Treatment Management Syste
03 - Precise Diagnostic Program
Because we understand women, LANTE DBGYN